Breast Cancer
Breast cancer affects both women and men, although women are more likely to get diagnosed. Breast cancer affects 27% of women who are diagnosed with the disease. Bookmark this blog to get an overall idea about breast cancer, its treatment, and its recovery steps.
What is breast cancer?
Breast cancer is caused by the abnormal growth of cells or tumours in the breast region. Lumps felt during self-examination are a common sign of breast cancer. Breast cancer cells are said to have metastasized when they spread to other parts of the human body.
Breast cancer is the most commonly reported cancer among women globally. In India, a woman is diagnosed with breast cancer every four minutes, according to a study by Globocon 2020. More young women in India are diagnosed with breast cancer compared to the US. Lack of awareness and late detection of breast cancer increases the mortality risk.
Where does breast cancer start?
The breast is an organ on the chest with glands, ducts, and fatty tissue. There is a left and right breast, and their size depends on the amount of fat tissue. The breast’s structure includes; lobules, ducts, and connective tissue. Lobules are the glands that produce milk and the ducts carry milk to the nipple. Layers of fibrous and fatty tissue form the connective tissue which holds the whole structure together. Breast cancer cells can grow in the ducts and lobules. Cancer cells spread to other parts of the body through blood and lymph vessels.
What are the notable signs and symptoms of breast cancer?
Early detection helps in handling the mortality rate of breast cancer. People can physically detect breast cancer by touching and feeling their breasts. A newly formed lump is the most common symptom of breast cancer.
These lumps tend to be painless hard masses with irregular borders. They can also be soft, spherical, or tender. However, it is important to note that not all lumps have to be cancer.
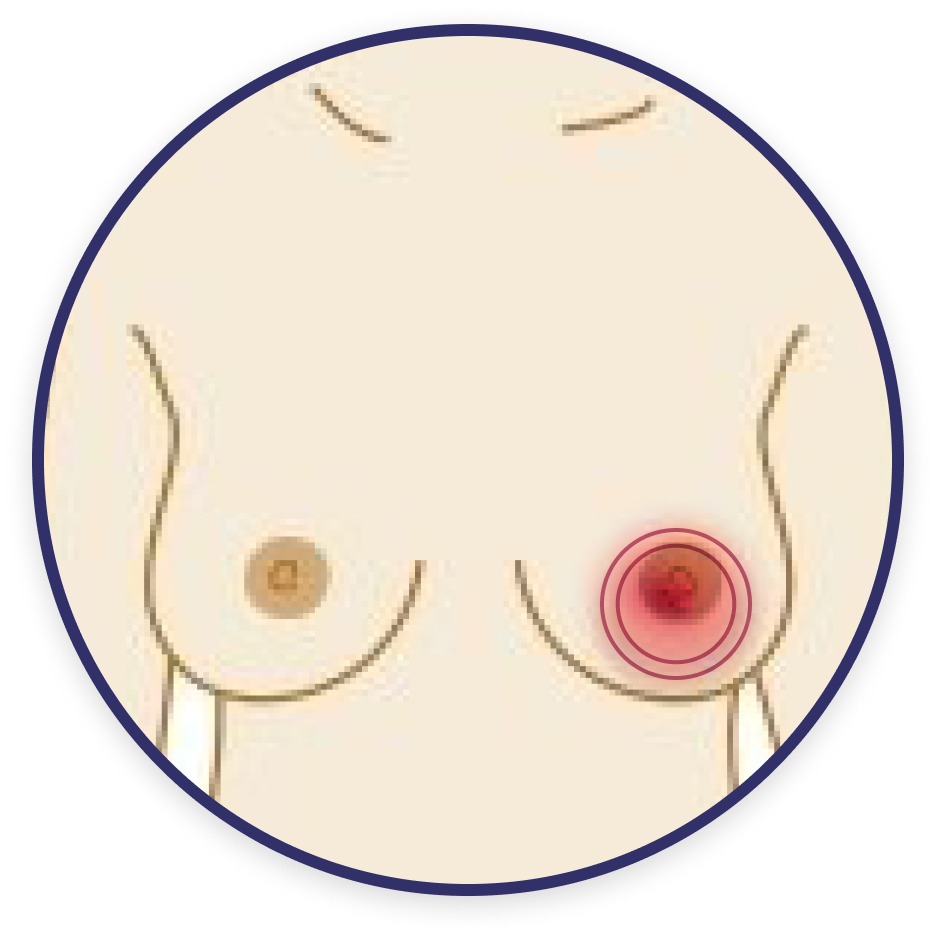
Redness or rash around the nipples/areola
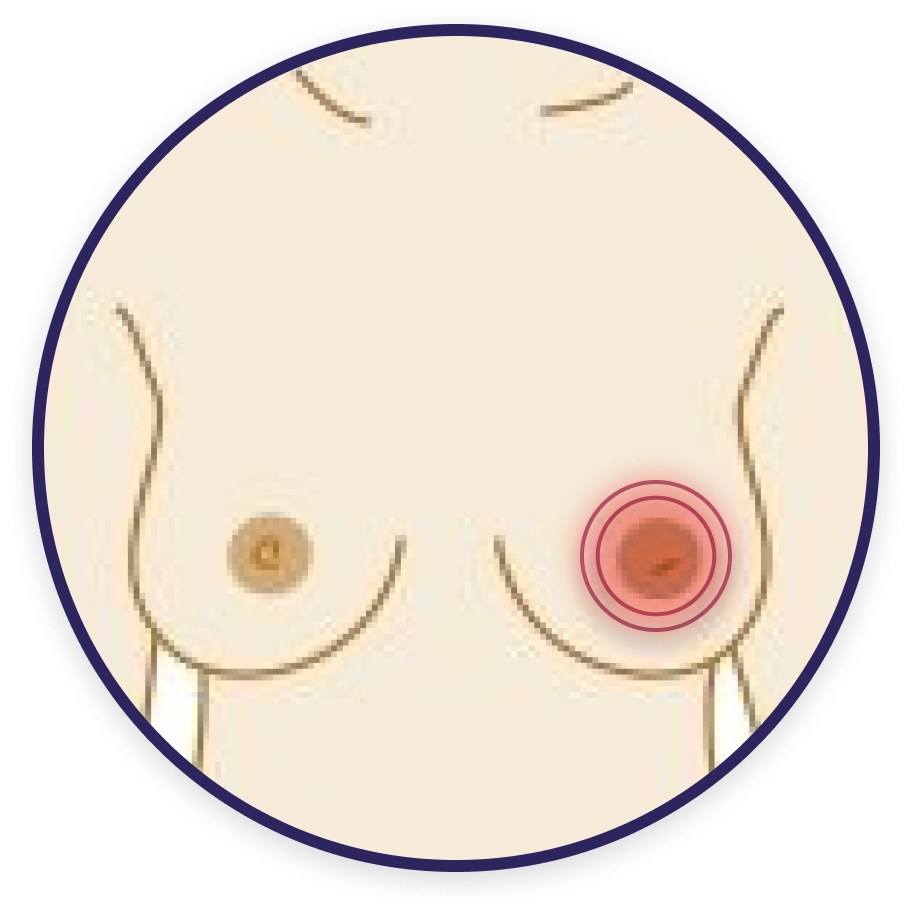
Change in size or shape of nipple
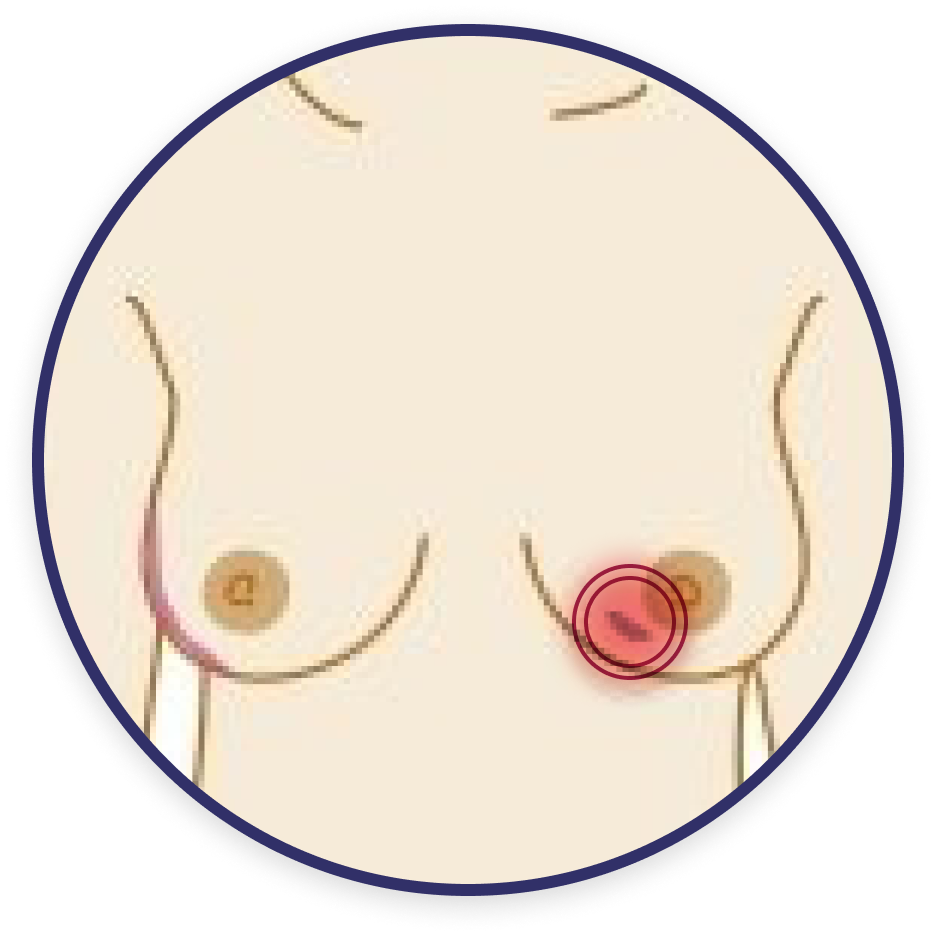
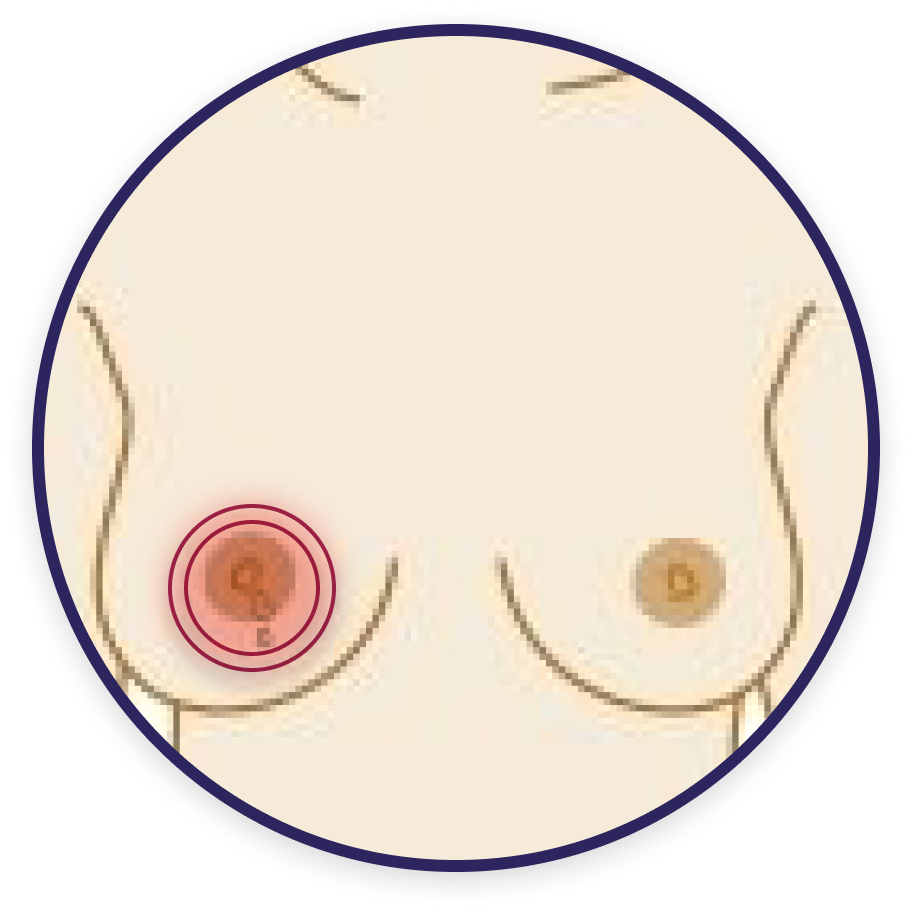
A lump or area that feels thicker
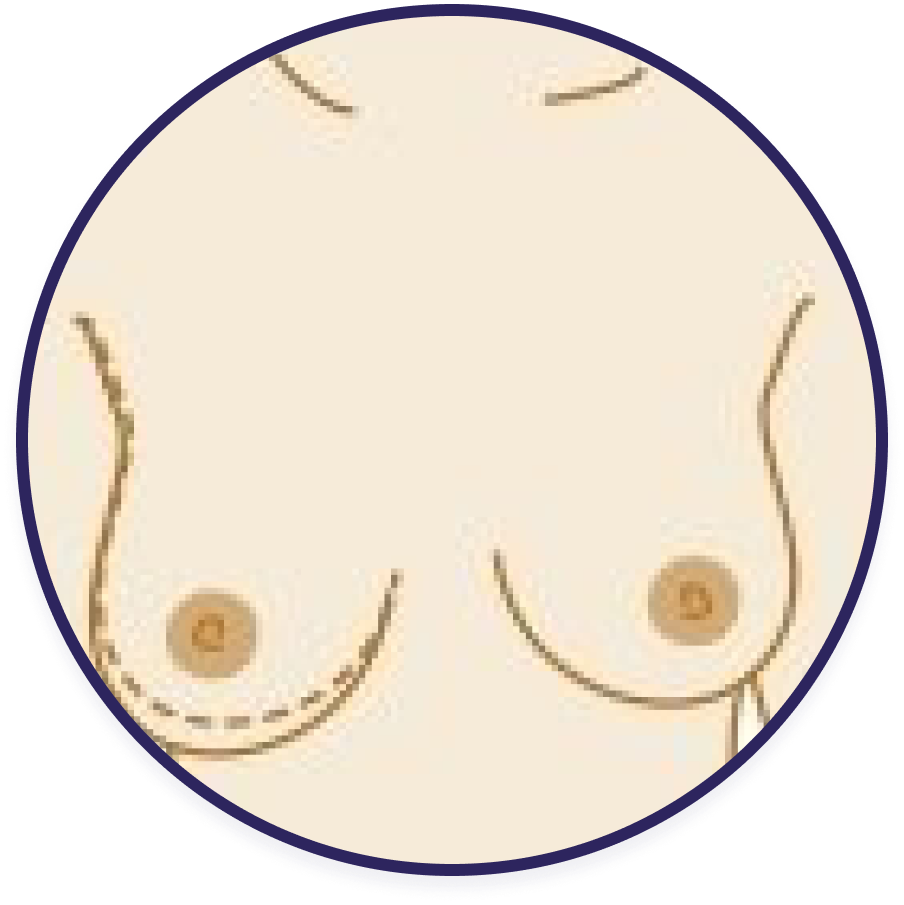
Change in size or shape
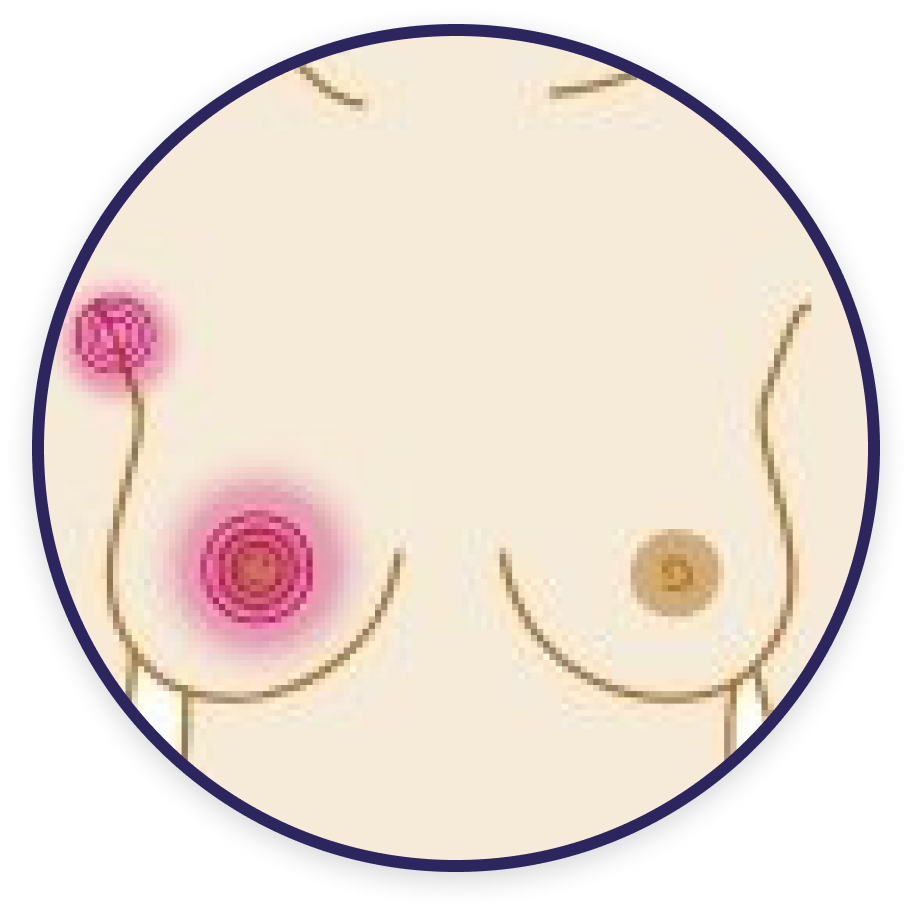
Pain in breast/armpit
Swelling in armpit
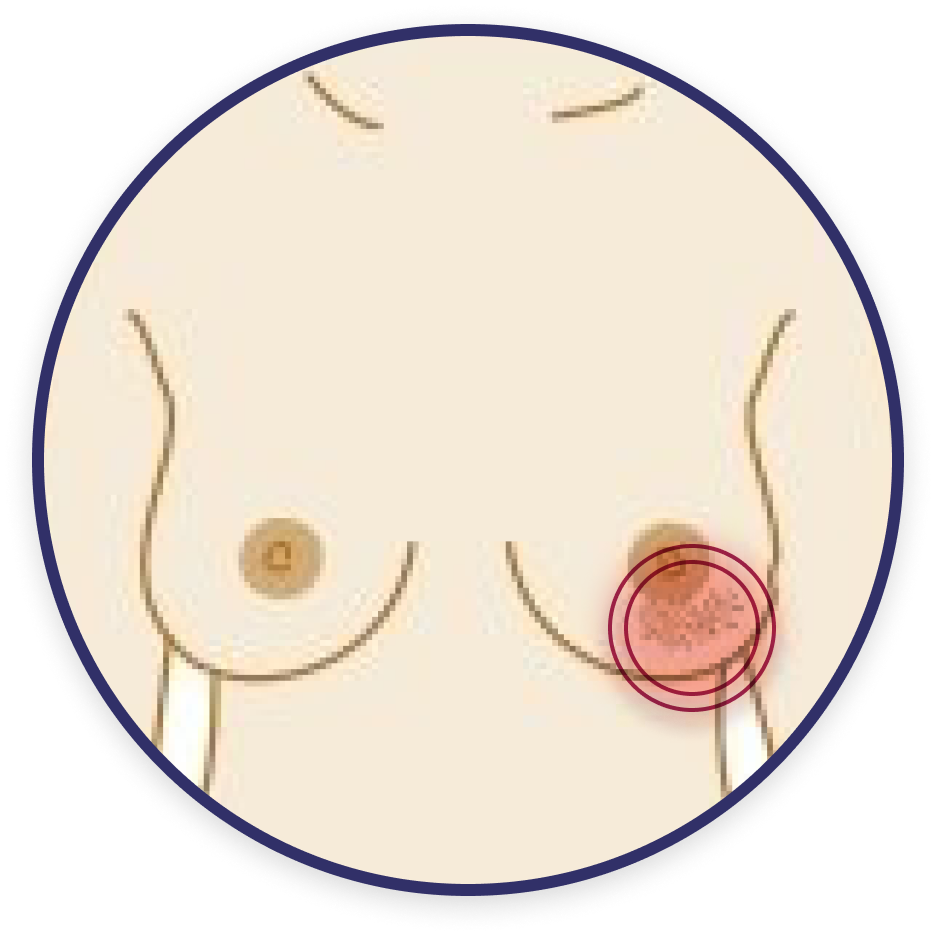
Change in skin texture
Discharge of liquid/blood
Do you suspect breast cancer? Take the evaluation right away!
What are the different types of breast cancer?
Breast cancer is primarily divided into two types; invasive and non-invasive. Tumour cells spread from the site of formation in invasive breast cancer. Because non-invasive cancer does not spread beyond the tissue from which it originated, it is referred to as carcinoma in situ (which means in place”). Breast cancer that is non-invasive is contained within the lobules or milk ducts.
Different types of non-invasive Breast cancers are as follows;
- Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) : This is a condition in which abnormal cells are discovered in the lining of a milk duct in the breast, but the cancer cells have not spread beyond the ducts into surrounding breast tissue. The most common type of breast cancer is ductal carcinoma in situ. Women are advised to begin treatment as soon as possible to avoid it becoming invasive.
- Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) : This is a condition in which cells within the breast’s milk-producing glands or lobules are abnormal. LCIS is not cancer, but it increases the cancer risk, so women should have regular checkups and treatment.
Different types of invasive Breast cancer types are as follows;
- Invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) : It is the most common form of breast cancer, reported in at least 80% of all breast cancer, according to statistics published in cancer.org. It is a malignant tumour that begins in the breast milk ducts and can spread to other parts of the body through the lymph nodes. Its symptoms include a lump in the breast, nipple discharge, and changes in the appearance of the breasts.
- Invasive lobular carcinoma : It is a condition where the breast’s lobules are affected. It is usually detected on imaging tests such as mammography, ultrasound, and MRI. According to the study published by cancer.org, one out of every ten reported breast cancer is an ILC.
Rare types of breast cancer
- Inflammatory breast cancer (IBC): It is an aggressive form of invasive breast cancer that causes symptoms such as redness and swelling as a result of cancer cells blocking the skin’s lymphatic vessels.
- Paget s disease of the nipple: It is a rare type of cancer that affects the nipple or the areola. Common symptoms include hard, lumpy or crusty nipples or the area around the nipples. It is also characterized by the redness, discharge or bleeding from the nipple and the appearance of a lump.
- Phyllodes tumour: It is a rare form of breast cancer where the tumour is formed in the connective tissue. Phyllodes tumours can be both benign or malignant.
- Metaplastic breast cancer (MBC): It is a rare type of breast cancer that can be more aggressive than others. It is characterised by the variety of cell types that make up the tumour, which makes MBC difficult to diagnose.
What are the different stages of breast cancer?
Breast cancer stages are classified based on the severity of the cancer and the extent to which it has spread to other body parts. The treatment course is determined by the cancer stage and the location of the tumour. The various stages of breast cancer are as follows;
- Stage 0: Abnormal cells are present in the breast ductal lining.The abnormal cells are present in the breast’s ductal lining. The survival rate is 100%.
- Stage 1: The tumour size is less than 1 cm and is present in the breast tissue. Cancer may have spread to some lymph nodes. The survival rate is 98%.
- Stage 2: The tumour size is over 2 cm and it has spread to nearby tissues and a few axillary lymph nodes. The survival rate is 88%.
- Stage 3: The tumour size is over 5 cm and has spread to wider areas of the breast tissue and several lymph nodes. The survival rate is 52%.
- Stage 4: Cancer has spread to other parts of the body, reducing the chance of survival down to 16%.
What are the different grades of breast cancer?
Breast cancer cells are given a grade after being removed and investigated in the laboratory. Grading is based on how closely the removed cancer cells resemble normal human cells. Grading aids in determining prognosis, and medical experts recommend appropriate treatment based on that.
Grade 1 or low-grade number : Cancer cells are slow growing but they are likely to spread to other parts. Most cells in the collected sample look like normal breast cells.
Grade 2 or intermediate grade number : Cancer cells are growing faster than grade 1 but slower than grade 3.
Grade 3 or high grade number : Cancer cells that look very different from the normal are growing at a fast rate, making them more likely to spread.
What is breast cancer TNM staging?
It is the common way that medical experts stage breast cancer in patients.
T - Tumour - It focuses on the tumours size and extend of it s growth.
N - Node - It focuses on whether the tumour has spread to the nearby lymph nodes.
M -Metastasis - It focuses on whether the tumour has travelled to distant sites.
Think you have breast cancer? Book a test now
How is breast cancer diagnosed?
- Breast exam
The doctor examines the breasts and lymph nodes in the armpit for lumps or other abnormalities.
- Biopsy
It involves the extraction of the core of tissue from the suspicious area with a specialised needle and X-ray guidance. Samples are then sent to the lab to determine whether they are cancerous or not.
- Mammogram
It is the X-ray of the breast that helps in diagnosing possible abnormalities.
- Breast ultrasound
It is a process that makes the use of sound waves to produce images of the breast to determine possible lumps or other abnormalities. It helps in determining whether the new breast lump is a mass or a fluid-filled cyst.
- MRI
The MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) machine uses a magnet and radio waves to create pictures of the breast to check for possible abnormalities.
- PET scan
A positron emission tomography (PET) scan is a type of imaging test that uses a tracer (a radioactive substance) to look for the spread of breast cancer. This tracer can help to identify the areas of cancer that doesn t show up in an MRI or CT scan.
Other methods used for breast cancer investigation
- Blood sample tests
- CBC test
- LFT
- Urine routine examination
- Iron profile
- Thyroid profile
- Lipid profile
- Vitamin B3 and D12
- RFT
- Electrolyte profile
Tumour markers like CA15 3 and CEA Serum are also used to predict the response of the treatment.
Other prominent testing methods
- HER2
- Oncotype Dx
- MammaPrint PAM50 (Prosigna)
- ER and PR
- Breast cancer Index
- Grade tests (to detect Breast cancer and their stages)
- Tumour features
Breast cancer diagnosis can cost between 90 and 1.25 lakhs. We offer packages that reduce it by 40-60%.
What are the various breast cancer treatment methods?
Doctors suggest treatment methods for breast cancer depending on various factors like;
- The tumour s subtype
- The tumour s stage
- Results of Genomic tests
- Patient s age
- Patient s menstrual health
- Patient s preferences
Various breast cancer treatment methods are as follows;
Surgical treatment
- Lumpectomy: Also known as breast conservative surgery, it is a procedure where only a part of the breast, infected by cancer, is removed. This surgery is recommended when the cancer is in its early stages and its spread is limited to only one area of the breast.
- Mastectomy: It is the surgical removal of the entire breast including the fatty tissues, ducts, globules and some skin areas. Mastectomy is either partial or complete
- Lymph node dissection (LND): It is the surgical removal of the lymph node that has been affected by the cancer cells (sentinel node biopsy and axillary lymph node dissection).
- Axillary lymph node dissection (ALND): It is the surgical removal of the underarm lymph nodes that have been affected by cancer cells and it is the standard initial approach for those who are clinically node-positive.
Medical treatment
- Chemotherapy: It involves the usage of drugs such as Anthracyclines to destroy the rapidly growing tumour cells.
- Immunotherapy: It involves either natural or man-made treatment processes that boost the human body s natural immunity to destroy the cancer cells.
- Hormone therapy: Also called hormone-inhibiting or blocking therapies, it involves the blocking of hormones such as Estrogen and Progesterone to prevent cancer cell growth.
- Targeted therapy: It involves a drug treatment where the abnormal cells are identified, targeted and then killed. Usually, certain proteins that aid in the growth of cancer cells are targeted and destroyed.
Radiation treatment
- Radiation therapy: The treatment method involves the use of high-powered beams of energy, such as X-rays and protons, to kill cancer cells. Side effects of radiation to treat breast cancer can last from three days to six weeks, depending on the stage and severity.
What are the different side effects of breast cancer treatment?
Breast cancer side effects occur due to the disease or due to the treatment methods. They are either long-term side effects or late side effects.
Some of the commonly reported side effects of breast cancer treatment are as follows;
- Fatigue
- Headache, pain or numbness (peripheral neuropathy)
- Dental issues
- Lymphedema
- Osteoporosis
- Musculoskeletal issues
- Infertility
- Cardiac issues
- Cataract
- Blood clot
- Absence of normal menstrual flow
- Menopausal symptoms
- Sexual health issues
- Possible memory loss (chemo brain)
The side effects specific to various breast cancer treatments are as follows;
- Targeted therapy : Side effects of targeted therapy are shortness of breath, liver damage, hand-foot syndrome and diarrhea.
- Hormone therapy : The treatment process involves blocking estrogen and progesterone so the side effects include hot flashes, mood changes, joint pain, dry vagina and night sweats.
- Immunotherapy : It involves enhancing the body’s natural immune system to fight cancer and it causes symptoms like fever, chills, headache, nausea, weakness and muscle aches.
- Chemotherapy : Some of the common side effects caused by chemotherapy drugs include nausea, hair loss, vomiting, fatigue, and loss of appetite. Premature menopause and nerve damage are also reported.
- Radiation therapy : High-powered energy beams like X-rays and protons can cause side effects like red rashes, skin reaction, nerve damage or hardness and swelling. Patients have often reported severe pain after lumpectomy and radiation. Muscle pain after radiation treatment is also reported
Manage yor breast cancer treatment side effects?
What are the supportive therapies for breast cancer?
Care for cancer survivors doesn t end with the completion of active treatment. There is a need for follow-up care where the healthcare team needs to check whether there has been any relapse, manage any side effects and oversee the overall health of an individual.
Along with a set of allopathic solutions prescribed by the doctor to manage side- effects, other options include acupuncture, aromatherapy, exercise, hypnosis, massage therapy, meditation, music therapy and yoga to overcome anxiety, stress, depression, chemotherapy induced nausea, fatigue, pain or sleep-related problems.
- Nutrition and diet
Maintaining an ideal weight, a healthy diet, regular exercise and avoiding alcohol and smoking can go a long way in preventing relapse. Diets low in fat and high in vegetables, fruits and fibre are recommended. Intake of more plant-based proteins and less animal-based proteins along with adequate intake of water for hydration should be sincerely followed. Click here for nutrition assistance
- Fitness
Aerobics and a moderate to a high-intensity exercise routine can help in increasing energy, reducing the risk of lymphedema, promoting sleep and preventing mood swings. Walking, cycling, swimming and doing housework are all beneficial for a fit mind and active body. Click here for fitness assistance
- Emotional Health
Guided imagery and Mindful meditation, basic breathing exercises and focusing on inner self-help in finding peace and coping with breast cancer, its related trauma and the fear of recurrence. Patients are also provided with career counselling, marriage counselling, grief counselling and other types of support to overcome the disturbing phase. Mothers who have toddlers are given advice about how to break the news to their children and extended family. Click here for counselling assistance.
- Unique therapies/Supportive care
Apart from medical and surgical treatments, therapies such as Flower bach, Mistletoe therapy, Tibetan therapy, Homeopathy and Ayurveda also play a crucial role in the treatment of breast cancer. These therapies aim to improve the life of patients and maintain their mental well-being which can help them recover. Click here for supportive therapy.
- Breast reconstruction
Women who underwent mastectomy can opt for breast reconstruction surgery which includes implant reconstruction, flap reconstruction and nipple reconstruction. Click here for breast reconstruction assistance
What lifestyle changes are people with breast cancer expected to make?
- Stress management is a crucial component of post-treatment care. Patients should surround themselves with positive and supportive people. They can use guided imagery, meditation, and yoga.
- Minimum of 7-8 hours long sleep is essential to improve health, weight, memory, and attention control.
- Avoid too much screen time before bed, and blue light from smartphones, T and backlit tablets affects sleep.
- Avoid stimulants like coffee, sugar and alcohol.
- Do regular exercise to keep the body and mind fit. Break prolonged sitting time by getting up every hour.
- Eat lots of fruits, vegetables, peas, whole grains, beans, lentils, nuts, and seeds. Include omega-3 and monounsaturated fats but avoid processed meat like hot dogs, sausages, sandwich meat, bacon, and salami.
- Avoid exposure to environmental toxins like tobacco smoke, asbestos, styrene (found in Styrofoam), formaldehyde, and tetrachloroethylene.
What are the important follow-up care steps after breast cancer treatment?
Follow-up care is essential to avoid the recurrence of breast cancer. The medical expert reveals how often a cancer patient needs to go through physical exams and blood tests. The oncologist screens patients for cancer recurrence and the development of secondary cancer. Apart from routine check-ups, patients are expected to maintain a health record to ensure seamless follow-ups. Doctors try to keep a tab on whether breast cancer shows up in routine blood work.
In conclusion
As Ann Jillian says. There can be a life after breast cancer, and the prerequisite is early detection. Thus, every woman should undergo regular examinations and take immediate action upon detection.
One should not fear or be ashamed to seek the much-required professional help. We understand that cancer is tough, and the journey is tougher. Built on the pillars of trust and empathy, our team will assist patients through these difficult times, make those steps easy for you and make sure you smile your way through recovery
For anything cancer care, anytime, anywhere:
- Call us on +91 77188 19099, and your CancerMitr will be at your service.
- Write to us at hello@cancermitr.com. We will get back to you within 24 hours.

