Ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is the third most commonly reported gynaecological cancer in India. It is also a leading cause of mortality among women. The challenge is that ovarian cancer is mostly hormone-dependent, with estrogen and progesterone influencing its progression. Bookmark this blog to learn everything you need to know about ovarian cancer, treatment, and other matters.
What is ovarian cancer?
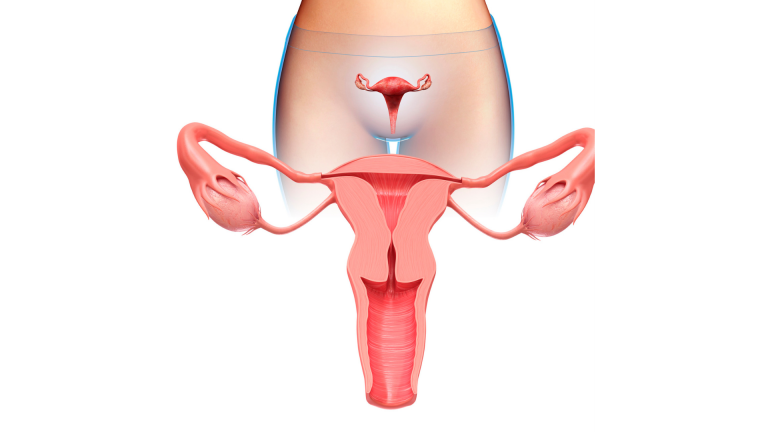
Ovaries are a pair of female glands located on either side of the uterus. The ovaries produce eggs or ova, and one egg is released every month, signalling a woman’s menstrual cycle.
Ovarian cancer is a condition where abnormal tumour cells form in the ovaries. Cancer cells destroy healthy body tissue, multiply aggressively and eventually spread to other parts of the human body, a condition known as metastasis.
Metastasis of ovarian cancer leads to the formation of tumours in the endometrium, breast, cervix, colon, and stomach.
Also read: Benign and malignant tumours: Why is it essential to understand the distinction?
Where does ovarian cancer start?
An ovary has three layers; the outer layer, middle layer, and innermost layer.
- The outer layer or cuboidal epithelium, is more or less like a capsule.
- The middle layer or cortex contains ovarian follicles and connective tissues.
- The inner layer or medulla contains neurovascular structures (blood and lymphatic vessels).
Two types of ligaments, the ligament of the ovary and the suspensory ligament of the ovary connect the gland to the uterus and pelvic wall, respectively. The egg from the ovaries goes into the uterus through a structure called a fallopian tube.
Depending on the structure, there are three types of ovarian cancer tumours;
- Epithelial tumours: These start in the cells that cover the epithelial gland.
- Germ cell tumours: These start in the cells that produce ova.
- Stromal tumours: Stromal tumours form in the structural tissue that holds the whole ovary together.
Apart from that, the tumours also form in the fallopian tube or epithelium of the uterus.
What are the notable signs and symptoms of ovarian cancer?
The biggest drawback of tumours that form in internal organs is that they are neither visible nor feelable. People should be aware of the signs and symptoms of ovarian cancer to ensure early diagnosis and treatment.
The layers of the colon wall are as follows;
- Discomfort in the lower abdomen
- Feeling bloating
- Swelling of the lower abdomen or hip region
- Pain during sex
- Unusual feeling of fullness when eating
- Unexplained or abnormal weight loss
- Frequent irritating back pain
- Fatigue or weakness
- Changes in bowel habits (constipation or diarrhoea
- Frequent urination (tumour presses the bladder)
- Abnormal bleeding from the vagina
- Shortness of breath (due to a build-up of fluid in the lungs)
What are the different ovarian cancer types?
Ovarian cancers are classified based on the cell from which the abnormal tumours originated.
The general classification of ovarian cancer is as follows;
- Epithelial ovarian carcinomas: It is the most commonly reported ovarian cancer and accounts for 85 to 90 percent of all ovarian cancers, according to research by the American Cancer Society. The danger of epithelial ovarian cancer is that since it is located on the ovary's epithelium (outer layer), it spreads to the lining and organs of the pelvis and abdomen. Then it spreads to the lungs, liver, and brain. Epithelial ovarian carcinomas are divided into four;
- Serous carcinomas: They are classified as either low-grade serous carcinoma or high-grade carcinoma based on how the abnormal cells look when compared to normal cells.
- Endometrioid carcinomas: These cancer cells divide slowly but spread fast because they often don’t respond to treatment.
- Mucinous carcinomas: It is a slow-growing cancer that is mostly seen in older women. It is rare and accounts for 6% of all reported ovarian cancers.
- Clear cell carcinomas: It is uncommon cancer that can be readily cured if detected early.
-
Germ cell tumours: They begin in the reproductive cells of women, which is the ova. According to American Cancer Society researchers, Germ cell cancer is rarely reported. Patients with germ cell tumours have a higher 5-year survival rate. The classification of the germ cell ovarian tumours is as follows;
- Teratomas: Teratomas can be either benign or malignant. These tumours tend to have structures like bone, muscle, and hair.
- Dysgerminoma: It is a rare ovarian cancer that divides and spreads slowly. But its metastasis leads to the formation of cancer in the central nervous system.
- Endodermal sinus tumour or the yolk sac tumour: It generally starts in the ovaries and is reported in children.
- Choriocarcinomas: It is rare cancer that tends to start in the placenta during the pregnancy period or in the ovaries.
-
Stromal cell tumours: Also known as sex cord tumours and sex cord-gonadal stromal tumours, it is rare cancer that accounts for 1 percent of all reported ovarian cancers, according to research. It starts in the stroma tissue cells that produce estrogen and progesterone.The subtypes of stromal cell tumours are as follows;
- Granulosa cell tumours
- Granulosa-theca tumours
- Sertoli-Leydig cell tumours
Vaginal bleeding is the most commonly reported symptom, and it is often found in its early stages. Therefore, post-menopausal women who experience vaginal bleeding should consult a doctor.
- Ovarian sarcoma: It starts in the connective tissues of ovarian cells, and the most common symptom is abdominal pain.
- Krukenberg tumours: These tumour cells quickly break away from their place of origin, multiply and spread. Therefore, it is considered metastatic or stage 4. The patient usually doesn't experience any symptoms in the early stages, but they experience gastrointestinal symptoms like change in bowel habits, bloating, etc.
-
Ovarian cysts: It is a condition where fluid-filled sacs develop in the ovaries. They are mostly benign and non-threatening, but they can turn into cancer.
What is ovarian cancer staging?
The staging process of cancer details how much cancer is there in the human body. Medical expert tailors the treatment process based on the cancer stage. In addition to that, a person’s chance of survival and frequency of treatment depends on the stage of cancer.
Ovarian cancer staging follows the TNM (Tumour, lymph Nodes, Metastasis).
-
Tumour (T):It checks the size of the tumour and whether it has grown outside the ovary or fallopian tube.
-
Lymph nodes (N):It checks whether cancer has spread to the nearby lymph nodes (in the pelvis or around the aorta).
-
Metastasis (M):It checks whether cancer has spread from it’s point of origin.
What are the different grades of ovarian cancer?
The grading of ovarian cancer refers to how similar the cancer cells look to normal cells. The grading process helps in determining how fast it grows and spreads in the human body. Treatment options are recommended based on both ovarian cancer stage and grade.
Ovarian cancer grades are divided into three;
Grade 1: Cancer cells are well differentiated and look like normal cells. They are likely to spread fast and recur.
Grade 2: Abnormal cells look somewhat like normal cells and will also spread fast and recur.
Grade 3: Cancer cells barely look like normal cells.
How is ovarian cancer diagnosed?
Imaging tests
- Ultrasound or ultrasonography
It is an imagining test where the sound waves are used to create an image on the video screen. It is an effective method to check whether the ovary has a solid mass or a fluid-filled cyst.
- Computed tomography or CT scans
It is an X-ray test that makes detailed imaging of the body, and it helps in determining whether the tumour has spread.
- Magnetic resonance imaging or MRI scans
It is a method that uses strong magnets to make the images. It is used to check whether cancer has spread to other parts, notably the brain and spinal cord.
- Positron emission tomography or PET scan
It is a process where radioactive glucose is administered into the human body to check how various cells are taking it up. Cancer cells take it up in big amounts when compared to normal cells.
- MRI
The MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) machine uses a magnet and radio waves to create pictures of the breast to check for possible abnormalities.
- PET scan
A positron emission tomography (PET) scan is a type of imaging test that uses a tracer (a radioactive substance) to look for the spread of breast cancer. This tracer can help to identify the areas of cancer that doesn t show up in an MRI or CT scan.
Other tests
- Laparoscopy
It is a procedure through which a doctor examines the ovaries and other pelvic organs and tissues using a thin, lighted tube. The images come on a monitor. The doctor makes a small incision or a cut in the abdomen for the process.
- Biopsy
It is an important procedure that helps confirm whether the tumour is benign or malignant. A small portion of the tumour is removed and then examined in the lab. For ovarian cancer patients, the biopsy is done during the surgery.
Other tests
If any of the previous tests detect a tumour then the patient is asked to go through a blood test to check for the RBC (red blood cells), WBC (white blood cells), and platelet count. Blood tests also help in determining whether the kidneys and liver is functioning properly. Ovarian cancers lead to high levels of tumour markers in;
- CA 125 test
- Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG)
- Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)
- Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
Estrogen and progesterone levels also tend to be abnormally high in ovarian cancer patients. ER-PR tests confirm whether the cancer is estrogen or progesterone positive.
Think you have ovarian cancer?
Take a look at our various screening and testing packages.
What are the various treatment methods for ovarian cancer?
Two of the most effective treatment options against ovarian cancer are surgery and chemotherapy.
-
Surgery
Ovaries, fallopian tubes, and other parts of the abdomen, spleen, etc., are surgically removed to prevent it’s further spread. Ovarian cancers can spread to the patient’s brain or spinal cord. If the tumour is hormone dependent, then the medical expert removes both ovaries to prevent the possibility of cancer’s spreading.
-
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is an effective treatment option against cancer. It is a process where powerful drugs are administered to the human intravenously. Most high-grade malignant tumours can be destroyed with the help of chemotherapy.
Other treatment options include radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and hormone therapy. As mentioned in the above paragraphs, the treatment options are determined based on the stage, grade, and spread of ovarian cancer.
Various ovarian cancer treatment methods are as follows;
-
Surgical treatment
- Ovaries, fallopian tubes, and other parts of the abdomen, spleen, etc., are surgically removed to prevent it’s further spread. Ovarian cancers can spread to the patient’s brain or spinal cord.
If the tumour is hormone dependent, then the medical expert removes both ovaries to prevent the possibility of cancer’s spreading.
-
Chemotherapy
- Chemotherapy is an effective treatment option against cancer. It is a process where powerful drugs are administered to the human intravenously. Most high-grade malignant tumours can be destroyed with the help of chemotherapy.
- Other treatment options include radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and hormone therapy. As mentioned in the above paragraphs, the treatment options are determined based on the stage, grade, and spread of ovarian cancer.
What are the side effects of ovarian cancer treatment?
The biggest drawback of surgical removal of ovarian cancer is infertility and early menopause. Chemotherapy affects the normal count of RBCs and WBCs.
Some of the common side effects of ovarian cancer treatment include;
- Infection
- Fatigue or weakness
- Hair loss
- Poor appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhoea or constipation
- Nerve problems; tingling of nerves, loss of control of hands and legs
- Chemo brain
- Sleep problems
- Sexual health problems
- Stress
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Excess sweating
What are the supportive therapies for ovarian cancer?
Cancer is a disease that takes a toll on an individual’s body and mind. At the same time, cancer treatment leads to a lot of side effects that affect a person’s ability to do day-to-day activities. As a result, cancer patients become dependent on others for basic routines like eating or going to the bathroom. Cancer treatment does not begin or end with surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, etc. Patients should undergo other forms of therapies that will help them cope with the side effects of the disease. Here are some of the important supportive therapy methods;
- Acupuncture
Cancer treatment methods like chemotherapy leads to side effects like nerves problem, loss of limb control, pain, nausea and vomiting. Acupuncture helps in relieving that to an extent.
- Acupressure
It helps in relieving severe fatigue experienced by ovarian cancer patients.
- Medication
Side effects like nausea, pain, fatigue, mood swings, etc., can be managed with suitable medication provided by doctors.
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy
Apart from medical and surgical treatments, therapies such as Flower bach, Mistletoe therapy, Tibetan therapy, Homeopathy and Ayurveda also play a crucial role in the treatment of breast cancer. These therapies aim to improve the life of patients and maintain their mental well-being which can help them recover. Click here for supportive therapy.
- Healthcare
Doctors suggest other methods like Flower bach, Mistletoe therapy, Tibetan therapy, Homeopathy and Ayurveda-based treatment to help ease the treatment side effects.
- Mental health counselling
Cancer patients go through severe stress, anxiety, and depression due to pressure and uncertainty. Mental health is as crucial as physical health, and some compassionate doctors assist patients.
- Fitness and physiotherapy
Cancer patients take time to get back on their feet following the treatment and the physical toll they suffer. Fitness experts and physiotherapists offer the required guidance for the same.
- Nutrition and diet
Nutrition experts and oncology dieticians suggest suitable diets for cancer patients to help them maintain their strength and ensure enough intake of all the essential nutrients; protein, fat, vitamins and minerals.
How to manage these side effects along with treatment?
CancerMitr provides a holistic treatment plan which involves supportive therapies to deal with pain, hair loss and other side effects. Check our website for various packages.
What lifestyle changes are people with ovarian cancer expected to make?
Chemotherapy tends to reduce the RBC and WBC counts, affecting normal immunity. Therefore, cancer patients should try to avoid infection as much as possible. Wash hands with a suitable disinfectant often. Stay away from big crowds to avoid possible infections.
Cancer patients who find it difficult to walk after chemotherapy or surgery can consider getting a walking cane or other walking aids.
Cancer patients should take enough rest and not push themselves too hard. At the same time, they should keep themselves active step by step. They can consider minor activities like folding clothes, arranging the room (without too much physical exertion or exposure to dust and other particles), reading books, listening to music, etc.
Consider physical activities like yoga or walking.
Chemotherapy leads to hair loss. Cancer patients should consider shaving their heads until the treatment is over. Hair loss as a side effect is mostly temporary, and people recover fast after treatment is over. Cancer patients can avail hats, wigs or scarves to cover their heads if they want.
Cancer patients should avoid alcohol consumption, smoking and chewing tobacco products.
Cancer patients should consume small portions of food frequently if they find it difficult to chew or swallow due to nausea.
Drink enough water for proper hydration. Drink ORS solution in case of diarrhoea.
In case of memory loss or chemo brain, keep a journal or a calendar to list all important activities, notably appointments.
What are the important follow-up care steps after ovarian cancer treatment?
Follow-up care is critical to avoiding ovarian cancer recurrence. Speak with a medical professional about how frequently physical examinations and blood testing should be performed.
The oncologist examines patients for ovarian cancer recurrence and secondary cancer growth. Patients are urged to keep a health record in addition to routine check-ups to facilitate smooth follow-ups. Doctors do their best to maintain track of whether ovarian cancer is detected in routine blood tests.
In conclusion
A cancer survivor stated, “it’s possible not just to survive but to thrive and live a healthy, wonderful life again.”
People should not bend their knees before cancer. However, there is hope, and one can put up a strong fight. There are solutions to all problems.
For anything cancer care, anytime, anywhere:
- Call us on +91 77188 19099, and your CancerMitr will be at your service.
- Write to us at hello@cancermitr.com. We will get back to you within 24 hours.

